Write Classification on Every Drawing Sheet
Draw and Write the record with Pencil only
Dear students, draw the diagrams neatly, if you don't understand in the post, search the same on the net and draw
ఆసిల్లటోరియా
P: Cyanobacteria
C: Cyanophyceae
O: Nostocales
F: Oscillatoriacea
G: Oscillatoria
G: Oscillatoria
- శాఖరహిత తంతురూపంలో ఉన్నాయి
- తంతువుల చూట్టు అతి పలుచని మ్యూసిలేజ్ తోడుగు ఉంది
- కణాలు పోడువు కన్నా వెడల్పుగా ఉన్నాయి
- హెటిరోసిస్ట్ లు లేవు
OSCILLATORIA
- Trichomes (filaments) are unbranched
- The trichomes are ensheated by a thin mucilage layer
- The cells are broader than length
- Heterocysts are absent
NOSTOC
P: Cyanobacteria
C: Cyanophyceae
O: Nostocales
F: Nostocaceae
G: Nostoc
- Several unbranched twisted filaments are embedded in a mucilage
- The cells in the filament are monoliform
- Heterocysts are intercalary
- Each heterocyst has two pores
నాస్టాక్
- అనేక శాఖరహిత, మెలితిరిగిన తంతువులు, జిగురు పోరలో ఇమిడి ఉన్నాయి
- తంతువులోని కణాలు పూస ఆకారంలో ఉన్నాయి
- హెటిరోసిస్ట్ లు మధ్యస్థ స్థానంలో ఉన్నాయి
- ప్రతి హెటిరోసిస్ట్ లో రెండు రంథ్రాలు ఉన్నాయి.

VOLVOX
C: Chlorophyceae
O: Volvocales
Sub O: Chlamidomonodina
F: Volvocaceae
G: Volvox
- The thallus is multicellular, motile and Coenobial
- The colony is hollow in the centre and the cells are arranged in single layer in the periphery
- The entire colony is surrounded by a mucilaginous sheath.
- The cells in a colony are pyriform in shape with two flagella.
- Each cell has a single cup shaped chloroplast.
వాల్వాక్స్
- థాలస్ బహూకణయుత, చలనసహిత, సాముహిక శైవలం
- సమూహంలోని కణాలు పరిధియంగా ఓకే స్థరంలో అమరి ఉన్నాయి
- సమూహం మోత్తన్నీ ఆవరించి ఓక జిగురు పోర ఉంది
- ప్రతి కణంలో ఓకే ఓక గిన్నే ఆకారంలోని హరిత రేణువు ఉంది.
OEDOGONIUM
C: Chlorophyceae
O: Oedogoniales
F: Oedogoniaceae
G: Oedogonium
- The thallus is multicellular, filamentous, unbranched
- The filaments are attached to the substratum with the help of a hold fast
- The cells are cylindrical in shape with a swollen upper end.
- Certain cells at their upper end may possess small, ring-like structures called ‘caps’.
- Each cell has many pyrenoids embedded in a reticulate chloroplast.
ఈడోగోనియం
- శాఖరహిత, తంతురూప, బహూకణయుత దేహాన్ని కలిగి ఉంది
- గద వంటి స్థాపనాంగ పీఠ కణంతో తంతువు ఆధారాన్ని అంటి పెట్టుకోని ఉంది
- తంతువులో కణాలు స్థూపాకారంగా ఉండి, పై భాగంలోని కణం శంఖు ఆకారంలో ఉన్నాయి
- కోన్ని కణాల చివర ఉంగరాల వంటి నిర్మాణాలు కనిపిస్తున్నాయి. వీటిని టోపిలు అంటారు.
- ప్రతి కణంలో అనేక పైరినాయిడ్ లు జాలాకారా హరిత రేణువులలో ఉన్నాయి
CHARA
C: Chlorophycea
O: Charales
F: Characeae G: Chara
- The thallus is macroscopic, branched and multicelluar.
- The thallus consists of a long, slender and erect main axis
- It is attached to the substratum by multicellular rhizoids.
- The main axis has nodes and internodes.
- The main axis has two types of branches (i) branches of unlimited growth and (ii) branches of limited growth.
- The internode is a long cylindrical single cell.
- The node has two central cells surrounded by 6-20 peripheral cells.
కారా
- థాలస్ స్థూలమైన, బహుకణయత, శాఖయుత నిర్మాణం.
- థాలస్ లో పోడవుగా, సన్నని, నిటారుగా పెరిగే మధ్య అక్షం ఉంది.
- మధ్య అక్షం బహుకణయుత మూల కేశాల ద్వారా ఆధారాన్ని అంటిపెట్టుకోన్ని ఉంది
- మధ్య అక్షం కణుపు, కణుపుమధ్యమాలుగా విభేదనం చెంది ఉంది
- మధ్య ఆక్షం పై 1. అపరిమిత వృద్ధి గల శాఖలు, 2. పరిమిత వృద్ధిగల శాఖలు ఉన్నాయి
- కణుపు మధ్యమాలు ఏకకణయుతంగా పోడవుగా, స్థూపాకారంలో నిర్మితమై ఉన్నాయి
- కణుపు రెండు కణాలతో నిర్మితమై, 6 నూండి 20 పరిధీయ కణాలను కలిగి ఉంది
ECTOCARPUS
C: Pheophyceae
O: Ectocarpales
F: Ectocarpaceae
G: Ectocarpus
1. The thallus is macroscopic, multicellular, filamentous and branched
2. The thallus shows heterotrichous habit, that is, it has a prostrate
rhizoidal system and an erect branched system.
3. The prostrate system is creeping and attached to the substratum.
4. The cells of the filament are uninucleate and rectangular.
5. The cells has discoid chromatophores.
ఎక్టోకార్పస్
- థాలస్ స్థూలంగా బహుకణయుత, తంతూయుత, శాఖయుతంగా ఉంది
- థాలస్ లో సాగిలబడే వ్యవస్థ, నిలువు వ్యవస్థలు ఉంది, విషమ తంతూరూపాన్ని కలిగి ఉంది
- సాగిలబడే వ్యవస్థ ఆధారం పై పోకుతూ ఆధారానికి అంటిపెట్టుకోన్ని ఉంది
- తంతువులోని కణాలు స్థూపాకారంగా, ఏక కేంద్రకంగా ఉన్నాయి
- కణంలో బిళ్ళల వంటి హరిత రేణువులు ఉన్నాయి
POLYSIPHONIA
C: Rhodophyceae
Sub C: Florideae
O: Ceramiales
F: Rhodopleodaceae
G: Polysiphonia
- The thallus is macroscopic, tufted feather like
- The thallus is heterotrichous.
- The erect system has the branches of unlimited growth and short branches called trichoblasts.
- The branches consists of a central siphon of elongated cells which are surrounded by pericentral siphon made of smaller cells.
- The cells of central and pericentral siphons are interconnected through pit connections.
పాలిసైఫోనియా
- థాలస్ స్థూలంగా కుచ్చు ఆకృతిలో ఈక వలె ఉంది.
- థాలస్ విషమ తంతూరూపాన్ని కలిగి ఉంది
- నిలువు వ్యవస్థలో అపరిమిత వృద్ధి గల శాఖలు, పరిమిత వృద్ధి శాఖలు లేదా ట్రైకోబ్లాస్టులు ఉన్నాయి
- శాలలో ఆక్షీయ నాళము మరియు దాన్ని ఆవరించి పరిధీయ నాళాలు (4-20) ఉన్నాయి
- పరిధీయ నాళాల కణాలు, ఆక్షీయ నాళ కణాలు గుంట సంయోజీతాలతో సంబంధం ఏర్పరుచుకోని ఉన్నాయి
Aim: To differentiate given bacteria to Gram +ve or Gram -ve.
Requirements:
Bacterial Cultures, Crystal Voilet(Primary Stain), Iodine solution (Mordant), 90% Alcolhol (Decolorising Agent), Safranin (Counter stain).
Procedure:
Clean the slide. By means of a sterile wire loop, transfer a drop of the
bacterial suspension to the centre of the slide.
Spread the drop over the centre of the slide and allow the fim to air dry.
Heat fix the sample to the slide by carefully passing the slide on a Bunsen
burner three times.
Add the primary stain crystal violet to the sample/slide and incubate for 1 minute.
Rinse slide with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds to
remove unbound crystal violet.
Add Gram's iodine for 1 minute- this is a mordant, or an agent that fixes
the crystal violet to the bacterial cell wall.
Rinse sample/slide with acetone or alcohol for ~3 seconds and rinse with a gentle stream of water. The alcohol will decolorize the sample if it is Gram negative, removing the crystal violet. However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells.
Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute.
Wash with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds.
If the bacteria is Gram positive, it will retain the primary stain (crystal violet) and not take the secondary stain (safranin), causing it to look violet/purple under a microscope.
If the bacteria is Gram negative, it will lose the primary stain and take the secondary stain, causing it to appear red when viewed under a microscope.
TMV
- The disease is caused by Tobacco mosaic virus.
- The first symptoms to appear are clearing of vein.
- Light green, dark green and yellow patches are formed
పోగాకు మోజాయిక్ వైరస్
- పోగాకు మెజాయిక్ వైరస్ వల్ల వ్యాధి కలుగుతుంది
- ముందుగా పత్ర ఈనెలు పసుపు పచ్చగా మారుతుంది
- పత్రం పైన లేత ఆకుపచ్చ, ముదురు ఆకుపచ్చ, పసుపు మచ్చులు కలిగి
- ఛిత్రవర్ణ వలె కనిపిస్తూన్నాయి
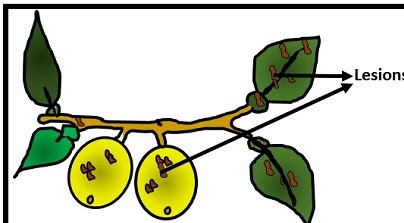
Angular leaf spot of cotton
Kingdom: Monera
Phylum : Proteobacteria
Class : Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Xanthomonadales
Genus: Xanthomonas
- The disease is caused by the bacteria Xanthomonas malvacearum.
- Dark green, watery soaked, angular lesions are formed on the leaves.
- The lesion later turn to angular brown to black lesions.
The little leaf of Brinjal
- The disease is caused by mycoplasma.
- The affected plant shows short, narrow, soft and yellowish leaves.
- The petioles are also reduced because of which the leaves appear to be sticking to the stem.
- The internodes are also shortened.
Try to Draw the small leaves as shown in the picture one
LEAF CURL OF PAPAYA
- This disease is caused by Virus
- Curling, crinkling and distortion of leaves
- Reduction of leaf lamina, rolling of leaf margins inward and downward,
- thickening of veins.
- Leaves become leathery, brittle and distorted. ...
బోప్పాయి ఆకు వక్రత
1. ఇది పైరస్ వల్ల వచ్చే వ్యాధి
2. పత్రాలు ముడుచుకుపోతాయి
3. పత్రాలు ఎగుడు, దిగుడుగా, లావుగా చర్మిలంగా ఉన్నాయి
4. మోక్కలు పోట్టిగా ఉన్నాయి
Citrus Canker
Kingdom: Monera
Phylum : Proteobacteria
Class : Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Xanthomonadales
Genus: Xanthomonas
Citrus canker is caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri
(syn. X. axonopodis subsp. citri).
The disease causes small, round blister-like formations on leaves, branches,
stems, new shoots and fruit.
Blister-like lesions on leaves and fruit start small and expand as the
disease progresses.
These lesions may darken to tan or black and develop a water-soaked
margin with a yellow halo surrounding it
Leaf blight of Rice
Kingdom: Monera Phylum : Proteobacteria Class : Gammaproteobacteria Order: Xanthomonadales Genus: Xanthomonas
Leaf Blight of Rice is caused by bacteria Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae.
Water-soaked to yellowish stripes on leaf blades or starting at leaf tips with a wavy margin
Leaves with undulated yellowish white or golden yellow marginal necrosis, drying of leaves back from tip and curling, leaving mid rib intact are the major symptoms.
Albugo conidia ఆల్బుగో కోనిడియం
Division: Eumycota
Sub Division: Mastigomycotina
Class : Oomycetes
Order: Paeronosporales
Family: Albuginaceae
Genus: Albugo
1. Rounded condia are arranged in a chain on the conidiophores..
2. The condia are formed in a basipetal manner and they are exogenous.
3. The conidia are attached to each other with the help of mucilaginous disjunctors.
4. Each conidium has 5-8 nuclei.
1. అనేక గోళాకార కోనిడియంలు గోలుసు వలె కోనిడియోఫోర్ పైన ఏర్పడ్డాయి
2. కోనిడియంలు ఆధారభిసార క్రమంలో బహిర్జాతంగా ఉత్పుత్తి అవుతాయి
3. కోనిడియంలు డిస్ జంగ్టర్స్ లేదా మధ్యస్థ చక్రాలనే జిగురు నిర్మాణాలతో
అతుకోని ఉన్నాయి
4. పత్రి కోనిడియంలో 5-8 కేంధ్రకాలు ఉన్నాయి
Albugo oospores ఆల్బుగు సంయుక్తబీజాలు
Division: Eumycota
Sub Division: Mastigomycotina
Class : Oomycetes
Order: Paeronosporales
Family: Albuginaceae
Genus: Albugo
- Oospores has two walls.
- The outer wall or exospores is thick and with small nodular structures.
- The inner wall or endospore is thin.
- సంయుక్తబీజం రెండు మంధమైన కణ కవచాలను కలిగి ఉంది
- వెలుపలి కవచం మందందాను. బుడిపెలతో ఉంది
- లోపలి పోర పలుచగా ఉంది
Mucor Vegetative మ్యూకర్ శాఖీయ నిర్మాణం
Division: Eumycotya
Sub Divsion: Zygomycotina
Class: Zygomycetes
Order: Mucorales
Family: Mucoraceae
Genus: Mucor
1. The Mycelium forms a loose fluffy mass of cotton on the substratum.
2. The mycelium is branched, coenocytic and aseptate.
3. Upright sporangiophores are also seen.
1. శిలింధ్రజాలం మెత్తని దూది వలె తెల్లగా ఉంది
2. తంతువులు విభాజక రహితంగా, శాఖయుతంగా, బహు
కేంధ్రకంగా ఉన్నాయి
Saccharomyces Vegetative
Division: Eumycotya
Sub Divsion: Ascomycotina
Class: Hemiascomycetes
Order: Endomycetales
Family: Saccharomycetaceae
Genus: Saccharomycetes
1. Saccharomycese is unicellular.
2. Each cell is oval or spherical.
3. The cell wall encloses the cytoplasm which is differentiated into
outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm.
1. ఏకకణ నిర్మాణం
2. కణాలు, గోళాకార లేదా అండాకారంగా ఉంటాయి
3. కణ కవచం లోపల కణద్రవ్యం దళసరి వెలుపలి పోరగా, పలుచని
లోపలి పోరగా విచక్షణ చెంది ఉంది
4. కణం పైన చిన్నబుడిపెలాగా ఏర్పడుతుంది
Saccharomycese Budding
Division: Eumycotya
Sub Divsion: Ascomycotina
Class: Hemiascomycetes
Order: Endomycetales
Family: Saccharomycetaceae
Genus: Saccharomycetes
1. Each cell give rise to one small small outgrowth or
protuberance called bud.
2. The bud gradually enlarges in size.
2. The bud gradually enlarges in size.
Pencillium conidia
Division: Eumycotya
Sub Divsion: Ascomycotina
Class: Ascomycetes
Order: Eurotiales
Family: Trichocomaceae
Genus: Penicillium
1. Branched, erect, conidiophores are seen like a small brush (Penicillus).
2. Each branch of conidiophores ends in sterigmata.
3. Sterigmata group of conidias basipetally.
4. Conidia are globose or ovoid, blue or green in colour and
appear like glass beads under the microscope.
1. పెన్సిలియమ్ లో బాగా అభివృద్ధి చెందిన శిలీంధ్రజాలం ఉంటుంది
2. అంతువులో కణాలు చిన్నవిగా ఓకటి నుండి అనేక కేంధ్రకాలను
కలిగి ఉంటుంది
3. నూనె చుక్కల రూపంలో ఆహరపు నిల్వ ఉంటుంది. అంతు కుడ్యం
పలుచగా ఉంటుంది.
ఖైటిన్ తో నిర్మితమై ఉండును
4. కోనిడియంలు గోళాకారం, అండాకారం, దీర్ఘ వృత్తాకారం లేదా
బేరిపండు ఆకారంలో ఉండ వచ్చును
Draw picture A and B Only
Penicillium Ascocarp
Division: Eumycotya
Sub Divsion: Ascomycotina
Class: Ascomycetes
Order: Eurotiales
Family: Trichocomaceae
Genus: Penicillium
1. Completely closed fruiting body called the cleisthothecium is seen.
2. Globose asci lie scattered in the fruiting body.
3. Each ascus has eight, uninucleate, wheel shaped ascospores.
1. ముఖ రంధ్రం లేని గోళాకార ఫలనాంగా కనిపిస్తుంది
2. దీని లోపల చెల్లా చెదురుగా ఆస్కస్ లు అమరి ఉన్నాయి
3. ప్రతీ ఆస్కస్ లోపల 8 ఏక కేంధ్రక, చక్రం ఆకారపు
3. ప్రతీ ఆస్కస్ లోపల 8 ఏక కేంధ్రక, చక్రం ఆకారపు
ఆస్కోస్పోర్ లు ఉన్నాయి
RUST ON WHEAT గోధుమపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు
Division: Eumycota
Sub Division: Basidiomycota
Class : Teliomycetes
Order : Uridinales
Family : Pucciniaceae
Genus : Puccinia
Write and Draw uredial and telial stages
in one page
External Feature
External Feature
- Rust on Wheat is caused by Puccinia graminis tritici.
- Dark Brown or black lesions are seen on the leaves, leaf sheaths and stem.
- The infected part gives rusty appearance due to these pustules.
- గోధుముపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు పక్సినియా గ్రామినిస్ ట్రిటికై వల్ల కలుగుతుంది
- పత్రం, పత్ర తోడుగు మరియు కాండం పైన ముదురు గోధుమ లేదా నల్లని మచ్చలు కనబడుతాయి
- స్ఫోటాల వల్ల వ్యాధి సోకిన భాగాలు తుప్పు పట్టినటుగా కనబడుతాయి
Internal Feature
- Rust on Wheat is caused by Puccinia graminis tritici.
- Brick red coloured, oval lesions are seen on the leaves.
- Uredosori are seen from the ruptured epidermis.
- Each Uredospore is binucleate, stalked and round to oblong in shape.
- గోధుముపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు పక్సినియా గ్రామినిస్ ట్రిటికై వల్ల కలుగుతుంది
- పత్రం పైన వరుపు, గుండ్రన్ని మచ్చలు కనబడతాయి
- తెగిన బాహ్యచర్మ నుండి యురిడియోసోరై కనబడుతాయి
- ప్రతి యురిడియో సిద్ధబీజం ద్వికేంద్రక, వృంతయుత, గుండ్రని నిర్మాణం
Uredial stage యురిడియల్ దశ .
- Red oval shaped pustules are seen on the leaves.
- Epidermis is ruptured due to underlying uredospores.
- Each uredospore is binucleate, stalked and oval shaped.
Telial stage పక్సీనియా టిలియల్ దశ
- Black, oval pustules are seen on the leaves.
- Epidermis is ruptured due to underlying teleutospores.
- Teleutospores are elongated, two celled structure.
- పత్రం పైన నల్లని, గుండ్రన్ని స్ఫోటాలు కనబడుతున్నాయి
- టిలిటో సిద్ధబీజాల వల్ల బాహ్యచర్మం తెగింది
- టిలిటో సిద్ధబీజాలు పోడువుగా, రెండు కణ నిర్మాణం
Draw 'B' & Ç Diagram only
Pycnidial stage పిక్నిడియల్ దశ
Draw and write pycnidial and aecial stage in
one page
- On the upper surface of the Barberry leaf a flask shaped pycnidium is seen.
- The Pycnidium has a pore called ostiole
- Orange coloured periphysis are seen adjacent to ostiole.
- The cavity of pycnidium shows many elongated uninucleate pycnidiospores.
- బార్బేరి పత్రం ఉర్ధ్వ బాహ్యచర్మం పై కూజాకార పిక్నిడియం కనబడుతున్నాయి
- పిక్నిడియం అగ్రభాగాన బయటికి ముఖరంధ్రంతో తెరుచుకోని ఉంది
- వీటిలో కోన్ని స్వీకార తంతువులు కనబడుతున్నాయి
- పిక్నిడియం లోపల అనేక పోడువుగా, ఏకకేంధ్రక పిక్నిడియో సిద్ధబీజాలు ఉన్నాయి.
Puccinia aecial stage ఏసియల్ దశ
- On the lower epidermis of the Barberry leaves cup shaped aecidium are seen.
- Each aecidium has a protective layer called peridium.
- At the base of aecidium many elongated sporophores are arranged in palisade like manner.
- Each sporophore cuts of small disjunctor and large acediospore.
- బార్బెరి పత్రం అధో బాహ్యచర్మం పైన కప ఆకార ఏసిడియంలు కనబడుతున్నాయి
- పత్రి ఏసిడియం ను ఆవరించి ఓక రక్షక పోర ఉంది, దీనిని పరిచర్మం అంటారు
- ఏసిడియం పీఠ భగాన అనేక స్పోరోఫోర్లు అమరి ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రి స్పోరోఫోర్ నుండి ఓక ఏసియో సిద్ధబీజం మరియు డిస్జక్టర్ ఎర్పడుతుంది.
WHITE RUST ON CRUCIFERS
D: Eumycota
S D: Mastigomycotina
C: Oomycetes
O: Peronosporales
F: Albuginaceae
G: Albugo
- The white rust of crucifers is caused by Albugo candida
- White or cream coloured pustules are seen on the surface of the leaf
- The epidermis is ruptured due to pressure of conidia
- The conidiophores are arranged vertically in a palisade manner
క్రూసిఫెరెలో తెల్ల కూంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు
- ఈ వ్యాధి ఆల్బుగో కాండిడా వల్ల కల్గుతుంది
- ఆతిథేయి ఆకులపైన, కాండం మీద తెల్లటి మచ్చలు ఏర్పడాయి
- దీని నుంచి సిద్ధబీజాశయ వృంతాలు ఓక క్రమ వరుసలో ఏర్పడాయి
- ఆతిథేయి పత్రాల బాహ్యచర్మం కింది భాగంలో శిలింధ్రజాలం కేంద్రీకృతమై ఉంది
RUST ON WHEAT
D: Eumycota
S D: Mastigomycotina
C: Oomycetes
O: Peronosporales
F: Albuginaceae
G: Albugo
External Feature
- Rust on Wheat is caused by Puccinia graminis tritici.
- Dark Brown or black lesions are seen on the leaves, leaf sheaths and stem.
- The infected part gives rusty appearance due to these pustules.
గోధుమపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు
- గోధుముపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు పక్సినియా గ్రామినిస్ ట్రిటికై వల్ల కలుగుతుంది
- పత్రం, పత్ర తోడుగు మరియు కాండం పైన ముదురు గోధుమ లేదా నల్లని మచ్చలు కనబడుతాయి
- స్ఫోటాల వల్ల వ్యాధి సోకిన భాగాలు తుప్పు పట్టినటుగా కనబడుతాయి
Internal Feature
1. Rust on Wheat is caused by Puccinia graminis tritici.
2. Brick red coloured, oval lesions are seen on the leaves
3. Uredosori are seen from the ruptured epidermis
4. Each Uredospore is binucleat, stalked and rond to oblong in shape
- గోధుముపై కుంకుమ తెగుళ్ళు పక్సినియా గ్రామినిస్ ట్రిటికై వల్ల కలుగుతుంది
- పత్రం పైన వరుపు, గుండ్రన్ని మచ్చలు కనబడతాయి
- తెగిన బాహ్యచర్మ నుండి యురిడియోసోరై కనబడుతాయి
- ప్రతి యురిడియో సిద్ధబీజం ద్వికేంద్రక, వృంతయుత, గుండ్రని నిర్మాణం
Tikka disease of Groundnut
D: Eumycota
C: Deuteromycetes
O: Moniliales
F: Moniliaceae
G: Cercospora
- Tikka disease of Groundnut is caused by Cercospora personata.
- Circular dark brown spots are seen on the upper surface of the leaf.
- Conidiophores are dark coloured, small, unbranched and aseptate.
- Conidiophores are arising in groups from the stroma.
- The Conidia are produced acrogenously.
- Conidia are long, inversely clavate and septate.
వేరుశనగ టిక్కా తెగుళ్ళు
Follow the instructions given in red colour
Marchantia
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
External Morphology
1. Plants are thalloid, dorsi-ventral and prostrate
- థాలస్ బల్లపరుపుగా, పృష్టోదర సౌష్టవంతో భూమికి సమాంతరంగా పెరుగుతుంది
- థాలస్ ద్విభాజీ శాఖీభవనాన్ని కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
- ప్రతి శాఖ అగ్రంలో ఓక ఖాతం లేదా నోక్కు ఏర్పడి ఉంది
Dorsal Surface
1. The dorsal side has a conspicuous midrib
2. Many polygonal areas with dot like structures are present.
3. The polygonal area represent the underlying air
dot like structure are the air pores
4. Many cup shaped structures are present along the midrib. These
5. The gemma cups contain gemmae, the vegetative reproductive
1. థాలస్ పృష్టతలం ముదురు ఆకుపచ్చ వర్ణంలోను ఉంది
2. థాలస్ పృష్టతలంలో ఓక స్పష్టమైన మధ్య ఈనె ఉంది.
3. థాలస్ పృష్టతలంలో నల్లని చుక్కలతో కూడిన బహుభుజాకార ప్రాంతాలు
4. ఇవి దిగువన గాలి గదులలో తెరుచుకుంటాయి.
5. థాలస్ మధ్యలో ఉన్న గాడి వెంట గిన్నెల లాంటి నిర్మాణాలు ఉంటాయి.
వీటిని జెమ్మాకప్పులు ఉంటారు
వీటిని జెమ్మాకప్పులు ఉంటారు
6. ఈ జెమ్మాకప్పులలో ఫిడేలు ఆకారంలో ఉన్న జెమ్మాలు ఉంటాయి
Ventral Surface
- The ventral surface bears scales and rhizoids along the midrib
- The rhizoids are of two types – (i) smooth walled and (ii) tuberculate
1. థాలస్ ఉదరతలంలో కేశాల లాంటి ఏకకణ మూలతంతువులు, బహుకణ
నిర్మితమైన పోలుసులు ఏర్పడతాయి.
2. మూలతంతువులు రెండు రకాలు 1. నున్నటి గోడలు కలవి, 2. బుడిపెల
లాంటి గోడలు కలవి.
3. ఉదరతలం గట్టుకూ ఇరువైపులా రెండు నుండి నాలుగు వరుసలల్లో బహుకణ
పోలుసులు ఏర్పడతాయి.
4. పోలుసులలో ఆంధోసైయానిన్ వర్ణద్రవ్యం ఉండటం వల్ల ఊదారంగులో ఉంటాయి.
Marchantia V.S of thallus
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
1. The vertical section of the thallus shows i) Dorsal photosynthetic
2. The photosynthetic region is bounded on upper side by upper
epidermis, which is single layered, green with compactly arranged
thin walled cells.
3. Below the upper epidermis is a horizontal layer of many air chambers
4. From the floor of each air chamber arise assimilatory or
photosynthetic filaments
5. The photosynthetic filaments are branched, chlorenchymatous
6. Below the photosynthetic region lies the ventral storage region
7. It is composed of compactly arranged, thin walled parenchymantous
cells.
8. The lower most layer of the storage region is the lower epidermis
which bears rhizoids and scales.
థాలస్ అంతర్నిర్మాణం
1. దీనిలో రెండు భాగలు కనిపిస్తాయి –కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ భాగము,
ఆహారం నిలువ చేసే భాగము.
3. కణాలు చతురస్రాకారంలో ఉండి వాటి వెలుపలి గోడలు మందంగా ఉన్నాయి.
4. ఉర్థ్వ బాహ్యచర్మం పైన అక్కడక్కడ పీపా ఆకారంలో ఉన్న వాయు రంధ్రాలు
ఉంటాయి.
5. ఉర్ధ్వ బాహ్యచర్మం కింద అనేక గలి గదులు ఓక వరుసలో అమరి ఉంటాయి.
6. గాలి గదుల పీఠ భాగం నుంచి హరిత కణాల వరుసలు ఏర్పడతాయి.వీటిలో
హరిత రేణువులు ఉంటాయి, కాబట్టి వీటిని హరిత తంతువులు లేదా
స్వాంగీకరణ తంతువులు అంటారు.
7. స్వాంగీకరణ మండలానికి దిగువన నిలవ చేసే భాగం ఉంటుంది. ఇది
మృదుకణజాలంతో ఏర్పడుతుంది.
8. థాలస్ ఉదర భాగాన్ని కప్పుతు అధోబాహ్యచర్మం ఉంది.
9. అధోబాహ్యచర్మ కణాల నుండి ఏకకణ నిర్మిత మూలతంతువులు,
7. స్వాంగీకరణ మండలానికి దిగువన నిలవ చేసే భాగం ఉంటుంది. ఇది
మృదుకణజాలంతో ఏర్పడుతుంది.
8. థాలస్ ఉదర భాగాన్ని కప్పుతు అధోబాహ్యచర్మం ఉంది.
9. అధోబాహ్యచర్మ కణాల నుండి ఏకకణ నిర్మిత మూలతంతువులు,
బహుకణ నిర్మిత పోలుసులు ఉన్నాయి.
Draw above first diagram for Thallus with Gemma cups
on same page (Picture 4 and them 3 only)
Marchantia Thallus with Gemma cups
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
1. Many cup shaped structures are present along the midrib.
2. The margin of the gemma cup is toothed and membranous
3. The gemma cups contain gemmae, the vegetative reproductive
4. Many club-shaped glandular hairs are found intermingled with the
gemmae
1. మధ్యఈనే ప్రాంతంలో అనేక చిన్న గిన్నలు లేదా కప్పుల వంటి నిర్మాణాలు
ఉన్నాయి. వీటిని జెమ్మా కప్పులు అంటారు
2. జెమ్మాకప్పులు ముడుతలున్న అంచులతో ఉన్నాయి
3. జెమ్మాకప్పు బోలుగా ఉంది, కప్పు పీఠ భాగంలో వివర్ణమైన అసంఖ్యకంగా
జెమ్మాలు ఉన్నాయి
4. జెమ్మాల మధ్య గదాకారంలో వంధ్య జిగురు కేశాలు ఉన్నాయి
V. S of Marchantia Thallus with Gemma Cups
1. It shows an goblet-shaped structure with an outer wall and central
cavity
2. The outer wall is differentiated into photosynthetic region and inner
storage region
3. From the floor of the central cavity arise numerous discoid gemmae
4. Intermingled with gemmae are many mucilage hairs.
1. పత్రి జెమ్మాకప్పు గిన్నె ఆకారంలో ఉంది, కవచాన్ని, మధ్యలో కుహరాన్ని
కలిగి ఉంది.
2. కవచం కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ భాగము, ఆహారం నిలువ చేసే భాగము గా
విభేధనం చెంది ఉంది
3. మధ్య కుహరం నుండి అసంఖ్యాక షీడెల ఆకారంలోని జెమ్మాలు ఏర్పడుతున్నాయి
4. జెమ్మాల మధ్య గదాకారంలో వంధ్య జిగురు కేశాలు ఉన్నాయి
Antheridiophore and L.S of antheridophore on same page
Marchantia Thallus with Antheridiophore
- It shows a long stalk bearing a disc-shaped receptacle
- The receptacle is flat and has 8 lobes.
- Each lobe has a single row of antheridia
- దీనిలో ఓక కాడ, కాడ చివర బిళ్ళ వంటి అధానము కనిపిస్తున్నాయి
- అధానంలో 8 తమ్మెలు ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రి తమ్మెలో ఓక వరుస ఆంథరీడియంలు ఉన్నాయి
Marchantia Antheridiophore L.S
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
1. It shows a long stalk bearing a disc-shaped receptacle
2. The receptacle is slightly convex.
3. The outermost layer of the receptacle is the epidermis,
which is interrupted by air pores.
4. The air pores open below into an air chamber which has
branched assimilatory filaments.
5. Alternating with air chambers, are antheridial cavities
6. Each antheridial cavity, that open by an antherial pore or ostiole,
has a single globular antheridium.
1. దీనిలో ఓక కాడ, కాడ చివర బిళ్ళ వంటి అధానము కనిపిస్తున్నాయి
2. అధానం పైభాగంలో వాయురంధ్రాలతో కుడిన బాహ్యచర్మం ఉంది
3. వాయురంధ్రాల కింది గాలి గదులు ఉన్నాయి. వీటిలో స్వాంగికరణ
తంతువులు ఉన్నాయి
4. గాలి గదులకు ఏకాంతరంగా ఆంథరీడియల్ కుహరాలు ఉన్నాయి
5. ప్రతి కుహరం ఓక పురుషబీజాశయంతో నిండి ఉంది. కుహరం సన్నటి
కాలవ ద్వారా తెరుచుకోంటుంది
Archegoniphore and L.S of archegoniophore on same page
Marchantia Thallus with Archegoniophore
- It shows a long stalk and a disc shaped receptacle
- The receptacle has 8 lobes and 9 rays
- Each lobe bears a single row of 12-14 archegonia
- దీనిలో ఓక కాడ, కాడ చివర బిళ్ళ వంటి అధానము కనిపిస్తున్నాయి
- అధానంలో 8 తమ్మెలు మరియు 9 రేఖలు ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రి తమ్మెలో 12-14 ఆర్కిగోనియం సముదాయం ఉంది
Marchantia Archegoniopohore LS
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
1. It shows a long stalk and a disc shaped receptacle
2. The receptacle is slightly convex.
3. The outermost layer of the receptacle is the epidermis,
which is interrupted by air pores.
4. The air pores open below into an air chamber which has
branched assimilatory filaments
5. In young receptacle archegonia are acropetally arranged and
are present on the upper side of the disc.
6. Due to the growth in the centre of the disc archegonia are shifted
towards lower side and are in inverted position
దీనిలో ఓక కాడ, కాడ చివర బిళ్ళ వంటి అధానము కనిపిస్తున్నాయి
1. అధానం పైభాగంలో వాయురంధ్రాలతో కుడిన బాహ్యచర్మం ఉంది
2. వాయురంధ్రాల కింది గాలి గదులు ఉన్నాయి. వీటిలో శాఖయుత
స్వాంగికరణ తంతువులు ఉన్నాయి
3. లేత దశలో ఆర్కిగోనియాలు అగ్రాభిసారక్రమంలో అధానంపై
నిట్టినిలువుగా అమరి ఉంటాయి
నిట్టినిలువుగా అమరి ఉంటాయి
4. తర్వాత అధానపు మధ్యభాగం పెరగడం వలన ఆర్కిగోనియాలు
కిందివైపుకు నెట్టబడి, తలకిందులవుతాయి
Marchantia Sporophyte V.S
Bryophyta
Hepaticae
Marchantiales
Marchantiaceae
Marchantia
1. The sporophyte is enclosed by three envelops i) calyptras,
ii) perigynium and iii) perichaetium (involucres)
2. It is differentiated into a foot, seta and a capsule
3. Foot is small and bulbous
4. Seta is middle and short, stalk like and cylindrical
5. Capsule is spherical with a single layered jacket
6. Inside the capsule spores and elaters are present
1. సిద్ధబీజదం మూడు తోడుగుల - కాలిప్ట్రా, పెరిగైనియం మరియు
పెరికీటీయం (ఇన్ వల్యుకర్) తో ఆవరించబడి ఉంది
2. ఇది పాదం, కాడ, గుళిక అనే మూడు భాగాలుగా విభేదన చెంది ఉంది
3. పాదం చిన్నగా, లశునం వంటి నిర్మాణం
4. కాడ పోట్టిగా, వృత్తాకరంగా ఉంది
5. గుళిక గోళాకరంగా ఉంది, ఏకకణ మందంగల కవచంతో ఉంది
6. గుళిక లోపల సిద్ధబీజాలు, మరియు సన్నటి కండి ఆకారంలో
గల ఇల్లేటర్లు ఉన్నాయి
Anthoceros
Division: Bryophyta
Class:
External Morphology
1. The plants are thalloid, dorsiventral and prostrate.
2. The thallus is dichotomously lobed
3. The dorsal surface of the thallus is smooth
4. The ventral surface bears numerous unicellular smooth
5. On ventral surface small bluish green spots are seen in which
filaments of blue-green algae Nostoc are present.
V S of Thallus
1. The thallus is several cell thick in the middle and becomes
thinner toward the margin
2. The thallus shows the upper epidermis and lower epidermis
3. In between these two layers uniformly lie parenchymatous cells
without any intercellular spaces
4. The cells contain large chloroplast with a single pyrenoid
5. On ventral side, the thallus show large mucilage filled cavities
which open outside by slime pores.
6. The cavities contain colonies of Nostoc
7. Numerous rhizoids arise from the cells of lower epidermis
1. కాండం మధ్య భాగం మందంగా మరియు కోన భాగాలు పలుచగా ఉన్నాయి
2. థాలస్ లో ఉర్థ్వ భాహ్యచర్మం మరియు అధో బాహ్యచర్మాలు ఉన్నాయి
3. వీటి మథ్యలో థాలస్ అంతటా కేవలం కణాంతరావకాశాలు లేని
మృదుకణజాలంతో ఏర్పడి ఉంది.
4. కణాలలో ఓక పెద్ద హరితరేణువు, దానిలో పైరినాయిడ్ ఉన్నాయి
5. థాలస్ అధోతలంలో జిగురుతో నిండిన కుహరాలు ఉన్నాయి. ఈ
కుహరాలు రంధ్రం ద్వారా బయటకు తెరుచుకుంటాయి
6. కుహరంలో నాస్టాక్ శైవలం సముహాలు ఉన్నాయి
7. అధో బాహ్యచర్మం నుండి అనేక మూలతంతువులు ఏర్పడ్డాయి
V S of Anthoceros Thallus with Antheridia
- It shows antheridia inside the antheridial chamber
- The roof of antheridial chamber is two layered
- The antheridia has a multicellular stalk and club shaped body
- The body has a single layered sterile jacket
- Inside the jacket there are many androcytes
ఆంథరీడియంతో ఆంథోసిరాస్ కాండం అడ్డుకోత
1. పురుషబీజాశయాలు థాలస్ పృష్టతలంలో ఉండే కుహరాల్లో
ఉన్నాయి.
2. ఈ కుహరాలను పురుషబీజాశయం కుహరాలు అంటారు
3. ఈ కుహరాలపై కప్పు రెండు వరుసల కణజాలంతో ఏర్పడి ఉంది
4. పురుషబీజాలశయాలు గద ఆకారంలో ఉన్నాయి
V S of Anthoceros Thallus with Archegonia
1. It shows archegonia embedded in the thallus with only
2. The archegonia are in direct contact with the thallus
3. The archegonia are flask shaped structure with a
4. The venter contains a ventral canal cell and
5.
2-4 cover cellsThe neck contain 4-6 neck canal cell with
ఆర్కిగోనియాతో ఆంథోసిరాస్ కాండం అడ్డుకోత
1. స్త్రీబీజాశయాలు థాలస్ పృష్టతలం కణజాలంలో
2. ఇవి కూజా ఆకారంలో ఉన్నాయి
3. నిలో ఉదరం, కంఠంగా విభెదనం చెంది
4. ఉదరంలో స్త్రీబీజ కణం మరియు ఉదర
5. కంఠంలో 4-6 కంఠకుల్యా కణాలు ఉన్నాయి
Anthoceros with sporophyte
1. The dorsal surface of the plant shows linear,
2.
bristles or horns, hence anthocerosThe sporophyte is cylindrical and appear like
is called hornworts.
3.
involucreThe base of sporophyte is enclosed by an
L.S of Anthoceros sporophyte
1.It shows lower foot, middle meristematic
2.
tissue of gametophyteThe foot is bulbous and is embedded in the
3.
seta but there is a meristematicIn between foot and the capsule there is no
zone which adds new cells to the capsule above
4. The capsule is distinguished into capsule wall,
columella
5. The capsule wall is 4-6 layered, the outermost
interrupted by stomata
6. The columella is the central part of the capsule,
vertical rows of cells, it extends from base to the top of the capsule
7. Surrounding the columella is a cylinder of sporogenous
extends from the base to the tip of the capsule
8. At the base of the capsule the sporogenous tissue is single
a little higher it is differentiated into spore mother cells and pseudo elater
mother cells
9.
are seen, in theA little higher tetrads of spores and many pseudo elaters
upper most region of the capsule separated spores and pseudo elaters are seen
2. The capsule wall is 4-6 layered.
3. The outermost layer is epidermis and it interrupted by stomata.
4. Beneath the epidermis the wall layers are
cells, which contain 1-2 chloroplasts
5. The columella is the central part of the capsule and appears as a
solid square
6. Surrounding the columella is a cylinder of sporogenous tissue
Polytrichum
Polytrichum with Sporophyte
- The Plant body shows rhizome, leafy shoot and sporophyte
2. The rhizome is covered by leaves and
3. The leafy shoot is aerial, erect consisting of
the stem and spirally arranged leaves
4. The leaves has a broad colourless membranous
base and a lanceolate limb
5. The limb consists of a broad dark green midrib and rudimentary wings
6. From the apex of leafy shoot sporophyte is seen
seta and capsule
T. S of Polytrichum Rhizome
- It shows a triangular outline with epidermis, cortex and central cylinder
2. Epidermis is single layered with thick walled cells
3. Cortex consists of 3-4 layers of thin walled cells.
4. It is interrupted by three hypodermal or radial strands,
which extend from the periphery towards the centre
5. The endodermis consists of radially elongated large
cells, and is discontinuous and consists of three arcs
separated by radial strands
6. The central cylinder consists of 2-3 layered
parenchymatous pericycle, which is discontinuous
like the endodermis
7. The central cylinder is trilobed and consists of steroids
and hydroids
8. The stereids are thick walled, elongated, while hydroids
are bigger, empty dead cells scattered in between the stereids.
9.
6-8 polygonal leptoids
10. The inner most layer of leptoids is separated from the central
cylinder by a single layer of parenchymatous amylom
T.S of Polytrichum Aerial stem
- It shows an irregular outline with indistinct epidermis,
cortex and central cylinder
2. The cortex is differentiated into thick walled outer
cortex and thin walled inner cortex
3. The inner cortex is followed by rudimentary pericycle
4. Inner to the pericycle is leptom mantle consisting of
sieve tube like cells
5.Below the leptom mantle is hydrom sheath or amylom
layer consisting of suberised cells rich in starch
6.
thin walled cells without cell contents
- The centre of the stem is occupied by hydrom cylinder, the
cells of which are thick walled
T. S of Polytrichum Leaf
- It shows a broad midrib and a reduced lamina(wing).
- The midrib is several cells thick in the centre and gradually merging into the wing.
- The lower epidermis is single layer of large cells,
inner to which are 1-2 layers of sclerenchymatous
4. The central part of the leaf is made up of thin walled
parenchyma cells with patches of scattered sclerenchyma.
5. From the upper surface arise numerous, parallel,
chlorophyll containing lamallae.
6. Each lamallae is 5-8 cells in height and one celled in
width, terminal cell is colorless and enlarged.
Polytrichum Antheridial Branch
- It shows group of antheridia surrounded by dull red colour
perigonial leaves.
2. The perigonial leaves consists of a broad sheathing leaf base
terminating in a pointed tip.
3. Intermingled with antheridia are multicellular hair like paraphyses.
4.
a club-shaped body.
5. The body has a single layered jacket surrounding a mass
of androcytes.
Polytrichum Archegonial Branch
- It shows group of archegonia surrounded by pericheatial leaves.
- Intermingled with archegonia are multicellular
hair like paraphyses.
3. Each archegonium is flask-shaped structure with a
broad venter and a long neck.
4. The venter has two layered wall and contains a
ventral canal cell and an egg cell.
5. The neck consists of six vertical rows of cells
and a row of neck canal cells.
L. S of Polytrichum Capsule
- It shows a sporophyte differentiated into foot,
seta and capsule.
2. The foot is dragger shaped composed of thin
walled parenchymatous cells.
3. The seta is long, slender structure differentiated
into outer epidermis, sclerenchymatours hypodermis,
parenchymatous cortex and a central cylinder.
4.
Tip of the seta is enlarged to form a bulbous apophysis,
it has outer epidermis, chlorophyllous tissue and a central
conducting strand.
5. Capsule has two distinct regions - theca and operculum.
6. Theca has an outer epidermis and several layers of
chlorophyllous cells.
7. Inner to the wall layers is an outer lacuna or air space
traversed by chlorophyll containing trabeculae.
8. Outer lacunae is followed by spore sac containing
archesporial tissue.
9. Inner side of the spore sac is followed by inner air
space or lacunae traversed by trabeculae
10. The central part of the capsule is occupied by
parenchymatous columella.
11. The apical part of the capsule has a cap like operculum
which is delimited from theca by a rim of diaphragm.
12. The distal end of the columella is extended into a epiphragm.
13. Arising from the periphery of the diaphragm is peristome
consisting of 32 or 64 peristomial teeth.
Polytrichum Protonema
1. It shows a branched, filamentous protonema - the juvenile phase of the
1. It shows a branched, filamentous protonema - the juvenile phase of the
polytrichum gametophytic generation.
2. It shows upright, green, chloronema filaments and colourless rhizonema
filaments.
3. The rhizonema filaments have oblique septa
4. Near the base of chloronema filaments buds are present.
Lycopodium with cone
1. The plant body shows a creeping rhizome which gives off
slender, elongated, serial branches
2. The branching is dichotomous
3. The stem and its branches are covered with small leaves
arranged in spiral phyllothaxy
4. The leaves are simple, sessile, lanceolate with broad bade
with single mid rib which doesn't reach the Apex
5. At the tip of branches the sporophylls are organised as strobili or cones
6. Each cone has a central axis around which numerous
sporophylls are arranged spirally
7. Sporangia are borne singly on the upper side of the
sporophylls
లైకోపోడియం శంకువుతో
- మోక్క దేహంలో పాకుతూ పెరిగే కోమ్ము, దాని నుండి నిటారుగా, సున్నితమైన, వాయుగత శాఖలు ఏర్పడతాయి
- ద్విభాజి శాఖీయభవనం చూపుతాయి
- కోమ్ము మరియు శాఖలపైన చిన్న పత్రాలు ఓత్తుగా సర్పిలాకారంగా అమరి ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రాలు సరిళంగా, వృంతరహితంగా, బల్లెం ఆకారంతో ఉండి, మధ్య ఈనె కలిగి ఉన్నాయి
- శాఖల కోన భాగంలో సిద్ధబీజాశయ పత్రాలు శంఖువులుగా ఏర్పడాయి
- ప్రతి శంకు కు మధ్య అక్షం, దాని చూట్టూ సర్పిలంగా సిద్ధబీజాశయ పత్రాలు అమరి ఉన్నాయి
- సిధ్ధబీజాశయ పత్రాల పృష్టభాగంలో పీఠం వద్ద సిద్ధబీజాయాలు ఏర్పడాయి.
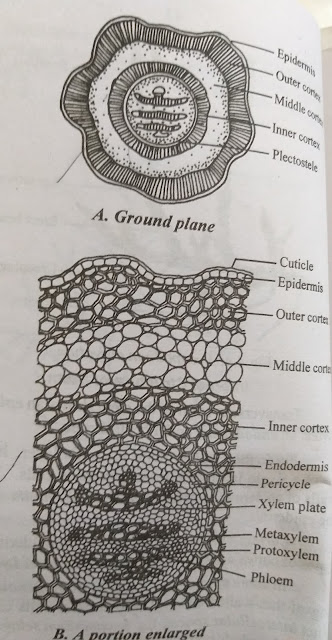
TS OF LYCOPODIUM STEM
- A cross section of the stem reveals epidermis, cortex and stele
- Epidermis is single layered with stomata
- The Cortex varies from species to species. In some the entire Cortex is parenchymatous. In other the Cortex is divided into outer and inner layers made up of thin walled sclerenchymatous and middle layer made up of thin walled parenchymatous cells
- Between Cortex and stele there is single layered endodermis with casparian thickenings
- Beneath endodermis is 3-6 layered pericycle made up of thin walled cells
- Stele is protostele with central mass of xylem surrounded by phloem
- Xylem is exarch
లైకోపోడియం కాండం అడ్డుకోత
1. కాండం అడ్డుకోత వర్తులాకారంగా ఉంది, బాహ్యచర్మం, వల్కలం, ప్రసరణస్తంభం
కనిపిస్తూన్నాయి
2. ఓకే వరుస బాహ్యచర్మంలో పత్రరంధ్రాలు కనిపిస్తున్నాయి
3. వివిధ జాతులలో వల్కలం వైవిధ్యాన్ని చూపుతుంది. కోన్ని
జాతులలో వల్కలంమంతా సరళమైన, ఓకే రకపు మృదుకణజాలంతో
నిర్మితమై ఉంటుంది, మరి కోన్ని జాతులలో మందమైన కణకవచాలు
గల బాహ్య మరిము అంతర వల్కలం మరియు పలుచని కణకవచాలు
గల మధ్య వల్కలము చూపుతుంది.
4. వల్కలానికి, ప్రసరణస్తంభానికి మధ్య ఏక కణ మందమైన అంత చర్మము ఉంది.
5. అంతశ్చర్మానికి దిగువున 3-6 కణాల మందం గల పరిచక్రము ఉంది.
6. ప్రసరణస్తంభం మధ్యలో ఘనాకార దారువు, దాని చూట్టూ పోషక
కణజాలం ఉంది – ప్రథమ ప్రసరణస్తంభం.
7. బాహ్యప్రథమ దారువు
2. Epidermis is single layered with thin walled cells and give rise to root hairs
3. Cortex is several layered with thick walled outer cortex and thin walled
T S OF LYCOPODIUM ROOT
1. The root is differentiated into epidermis, cortex, stele2. Epidermis is single layered with thin walled cells and give rise to root hairs
3. Cortex is several layered with thick walled outer cortex and thin walled
parenchymatous inner cortex
4. The stele may be monoarch or diarch
4. The stele may be monoarch or diarch
5. The xylem is C or U shaped with protoxylem at the tips of the curve
- లైకోపోడియం వేరు అడ్డుకోత
- వేరు అడ్డుకోతలో బాహ్యచర్మం, వల్కలం, ప్రసరణస్తంభం విభేదన కనబడుతుంది.
- బాహ్యచర్మం ఏక కణ మందంలో ఉంది, కణకవచాలు పలుచగా ఉన్నాయి, వాటి నుండి మూలకేశాలు ఏర్పడాయి.
- వల్కలం అనేక కణ మందంలో ఉండి, మందమైన కవచాలు గల బాహ్య వల్కలం మరియు పలుచని కవచాలు గల మృదుకణజాలయుత లోపలి వల్కలంగా విభేదన కలిగి ఉంది.
- ప్రసరణస్తంభం ఏక లేదా ద్వి దారు యుతం
- దారువు C లేదా U ఆకారంలో ఉంది.
T S OF LYCOPODIUM LEAF
- The T. S of leaf shows epidermis, mesophyll and vascular bundle
- The epidermis is single layered with stomata on both the surfaces
- The mesophyll is made up of uniform green parenchymatous cells
- The vascular bundle has central mass of xylem surrounded by phloem
లైకోపోడియం పత్రం అడ్డుకోత
- పత్రం అడ్డుకోతలో బాహ్యచర్మం, పత్రాంతరం మరియు నాళికా పుంబం కనబడుతున్నాయి
- బాహ్యచర్మం ఏక కణ మందంలో ఉంది, బాహ్యచర్మం రెండు తలాలో పత్రరంధ్రాలు ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రాంతరం విభేదన లేకుండా ఓకే రకమైన ఆకుపచ్చన్ని మృదుకణజాలంతో ఏర్పడి ఉంది.
- నాళికా పుంజం మధ్యలో దారువు, దాని చుట్టూ పోషక కణజాలం ఉంది.
L S OF STROBILUS
- The L S of cone shows a central axis on which the sporophylls are spirally arranged
- Each sporophyll bears a sporangia at its base on the adaxial side
- The sporangia are kidney shaped with a short stalk
- The sporangial wall is several layered inside which spores are present
లైకోపోడియం శంఖువు నిలువు కోత
- శంకువు నిలువు కోతలో కేంధ్ర అక్షం దాని చూట్టు సర్పిలింగా అమరి ఉన్న సిధ్ధబీజాశయ పత్రాలు ఉన్నాయి
- సిధ్ధబీజాశయ పత్రం పృష్ట భాగంలో పీఠం వధ్ధ ఓక సిధ్ధబీజాయం ఉంది
- ప్రతి సిధ్ధబీజాయం ఓక చిన్న వృంతంతో మూత్రపిండాకారంలో ఉంది
- సిధ్ధబీజాశయగోడ అనేక వరుసలో ఉండి, దాని లోపల సిధ్ధబీజాలు ఉన్నాయి
EQUISETUM
External Morphology
- The plant shows an underground rhizome and aerial stem
lower side
3. The aerial stem is cylindrical, stiff and jointed with distinct
nodes and internodes
4. The internodes are long, hollow and ridged
5. The aerial stem has two types of branches, sterile and
fertile branches
6. Sterile branches are green with whorl of scale leaves and lateral
branches at each node
7. Fertile branches are unbranched, non green and terminate into
strobilus at the apex
8. The leaves are small, scale like, fuse laterally forming a sheath
appressed to the node
9. Each strobilus is composed of an central axis from which arises a
whorl of stalked, peltate sporangiophores
ఈక్వీజిటమ్ శంకువుతో
- మోక్క దేహంలో భూగర్భ, బహు శాఖయుత కోమ్ము, దాని నుండి వాయుగత శాఖలు ఏర్పడున్నాయి
- కోమ్ము కణుపు, కణుపుమధ్యమాలు గా విభేదనం చెంది ఉంది. కణుపు పై భాగం నుండి వాయుగత శాఖలు, కింది భాగం నుండి వేళ్ళు ఏర్పడాయి
- వాయుగత కాండం గోళాకారంగా ఉంది, అతుక్కునట్లుగా ఉంది, కణుపు, కణుపుమధ్యామాలుగా విభేదనం చూపుతుంది
- కణుపు మధ్యమాలు పోడువుగా, బోలుగా మరియు గరుకుగా ఉన్నాయి
- వాయుగత కాండం పైన వంధ్య శాఖలు మరియు ఫలవంతమైన శాఖలు ఏర్పడ్డాయి
- వంధ్య శాఖలు ఆకుపచ్చగా ఉంది, వాటి కణుపుల నుండి పోలుసాకులు మరియు పక్క శాఖలు ఓక వలయంలో ఏర్పడి ఉన్నాయి
- ఫలవంతమైన శాఖలు వర్ణ రహితంగా, శాఖ రహితంగా ఉండి, వాటి కోన భాగంలో శంఖులు ఏర్పడి ఉన్నాయి
- పోలుసాకులు చిన్నవిగా ఉండి, పీఠ భాగంలో సంయుక్తమై, ఓక తోడుగు వలే ఏర్పడ ఉన్నాయి
- పత్రి శంఖువులో ఓక కేంధ్ర అక్షం ఉండి, దాని నుండి
T S OF ROOT
- It shows epidermis, cortex and stele
- Epidermis is single layered with root hairs
- Cortex is divided into an thick walled outer cortex and parenchymatous inner cortex
- Endodermis is two layered
- Stele is tri - tetra arch
- Single large metaxylem in the center with 3-4 protoxylem surrounding it
T S OF STEM
1. The T S of stem is wavy in outline with ridges and furrows
2. The outer most layer is epidermis, the cells are deposited with silica
2. The outer most layer is epidermis, the cells are deposited with silica
and is covered by thick cuticle
3. Beneath epidermis highly differentiated cortex is present
4. The outer cortex beneath the ridge is made up of sclerenchyma and
3. Beneath epidermis highly differentiated cortex is present
4. The outer cortex beneath the ridge is made up of sclerenchyma and
beneath the furrow is made up of chlorenchyma
5. The inner cortex consists of thin walled parenchyma cells.
5. The inner cortex consists of thin walled parenchyma cells.
It shows large air filled cavities called Vallecular canal below the furrows
6. Endodermis is single layered followed by single layered pericycle
7. The stele is ectophloic siphonostele
8. Vascular bundle are collateral, conjoint, endarch and closed
6. Endodermis is single layered followed by single layered pericycle
7. The stele is ectophloic siphonostele
8. Vascular bundle are collateral, conjoint, endarch and closed
present below the ridges
9. The protoxylem tracheids form a cavity called carinal canal
9. The protoxylem tracheids form a cavity called carinal canal
10. Inner to the ring of Vascular bundles, a large hollow pith is present
కాండం అడ్డుకోత
కాండం అడ్డుకోత
2. ఇది బాహ్యచర్మం, వల్కలం, ప్రసరణస్తంభంగా విభేదనం చేంది ఉంది
3. బాహ్యచర్మం ఏక కణ మందంలో ఉండి, వాటి వెలుపలి గోడలపై సిలిక పూత ఉంది
మరియు మందమైన అవభాసినితో కప్పి ఉంది
4. బాహ్యచర్మం కింద విశాలమైన విభేదనం చెందిన వల్కలం ఉంది
5. గోప్పుల కింద వెలుపలి వల్కలం ధృడకణజాలంతోను, గాడుల కింద
హరితమృదు కణజాలంలో ఏర్పడి ఉంది
6. లోపలి వల్కలం పలుచని కవచాల గల మృదుకణజాలంతో ఏర్పడి ఉంది.
గాడుల కింద లోపలి వల్కలంలో గాలితో నిండి ఉన్న వాలేక్యులార్ కాలవలు ఉన్నాయి.
7. అంత చర్మం మరియు పరిచక్రం ఏక కణ మందంలో ఉన్నాయి
8. ప్రసరణస్తంభం నాళాకార ప్రసరణస్తంభం
9. నాళిక పూంజాలు గోప్పుల కింద ఉన్నాయి. ఇవి సంయుక్తం, సహపార్శ్వ,
అంతరప్రథమ దారుకం మరియు ఆవృతం.
10. నాళిక పుంజాల లోపల దవ్వ ఉంది
10. నాళిక పుంజాల లోపల దవ్వ ఉంది
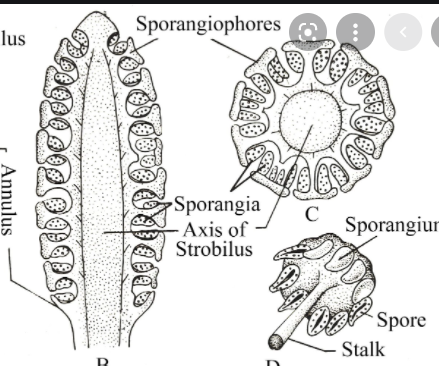
EQUISETUM L S OF STROBILUS
1. Each strobilus is composed of an central axis from which arises
whorl of stalked, peltate sporangiophores
2. Each sporangiophore is an umbrella-like structure with a slender
stalk bearing a peltate and hexagonal disc
3. The disc is at right angles to the stalk and has 5-10 sporangia on the
underside facing the central axis
4. Below the whorls of sporangiophores, the central axis bears a
ring-like outgrowth called the annulus
శంఖువు నిలువు కోత
వృంతాలు ఏకాంతర వలయాలుగా అమరి ఉన్నాయి
2. ప్రతి సిధ్ధబీజాశయ వృంతం ఛత్రం వలే ఉండి, శాఖ రహిత కాడ,
దాని చివర షడ్బుజాకార ఫలకం కలిగి ఉంది
3. ఫలకం శంఖు అక్షం పై లంబంగా ఉండి, కింది భాగంలో
5-10 సిధ్ధబీజాశయాలను కలిగి ఉంది
శంఖు పీఠ భాగంలో పత్రాలు సంయుక్తమై, గిన్నె వంటి వలయమైన అన్యూలస్ లేదా కాలర్ ను ఏర్పరుస్తాయి.
Marsilea with Sporocarp
External Morphology
- The plant is differentiated into rhizome, leaves and roots
- Rhizome is slender, creeping and differentiated into nodes and internodes
- From the node, leaves arise on the upper side, and adventitious roots arise from the lower side.
- The leaves are compound and four leaflets or pinnae arise on the tip of the long petiole.
- The leaflets are obovate and venation is dichotomous
- The sporocarp are borne on the petiole just above the base
- The sporocarp are stalked and bean shaped
Marsilea Rhizome
2. Epidermis is outermost layer made up of single row of cells, stomata are absent.
3. Cortex is differentiated into three distinct regions i.e., outer, middle and inner cortex.
4. The outer cortex is parenchymatous and consists of a ring of air chambers seperated by
parenchymatous septa. This region is called as arenchyma.
5. Middle cortex is sclerenchymatous.
6. Stele is amphiphloic solenostele. Xylem is in form of a ring sorrounded on both
sides by phloem.
Marsilea Petiole
1. A Transverse section of petiole shows epidermis, cortex and stele.
2. Epidermis is the outermost layer made of rectangular cells.
3. Cortex is differentiated into outer and inner cortex.
4. Outer cortex consists of closely placed parenchymatous cells.
5. Below the parenchyma there are air chambers separated by septa.
6. Inner
cortex is parenchymatous.
7. The
stele is triangular in shape. Xylem is arranged in V shape with exarch protoxylem.
8. The V-shaped mass of xylem is surrounded by phloem and single-layered pericycle successively.






























































No comments:
Post a Comment